The terms ‘Digital signatures’ and ‘electronic signatures’ are normally used interchangeably, but they are not the same. Both have different applications, rely on different technologies, and offer varying levels of legal security. These are used to authenticate documents electronically, but the technology they use for confirming authenticity and maintaining document integrity sets them apart.
A digital signature is more secure type of electronic signature that confirms a signer’s real identity and guarantees that no changes have been made to the document once it gets signed. On the other hand, an electronic signature has a broader definition. It can be as simple as typing your name, or uploading scanned signatures that show your approval.
In this article, we will explore both signature types in detail. We will compare their functionalities and point out the differences in legal and technical aspects. This will help decision makers decide upon the most suitable option for their work processes.
Aspect | Digital Signature | Electronic Signature |
Core Focus | Uses cryptographic algorithms to confirm signer identity and document integrity | Represents consent or approval via electronic means, such as typed names or scanned images |
Main Functionalities | Provides encryption, certificate validation, and tamper detection for signed documents | Enables simple sign-off and acknowledgment on digital forms or agreements |
Business Stage Fit | Suitable for medium to large businesses, highly regulated industries, or any organization handling sensitive documents | Fits businesses of all sizes, especially where speed and convenience are priorities |
Primary Value | Ensures strong legal enforceability, high security, and compliance with legal standards | Saves time, improves workflow efficiency, and simplifies document approvals |
Implementation Time | May take days to weeks due to certificate setup and system integration | Usually immediate or within a few hours using cloud-based platforms |
A digital signature is a specific form of electronic signature that uses encryption technology to prove a document is original. It confirms the signer’s identity and makes sure that the document hasn’t been modified after signing.
Digital signature works with Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), where each signer receives a unique digital certificate from a trusted authority. This mechanism adds advanced security measures and makes them legally binding in most countries. Due to this reliability, digital signatures are suitable for confidential or high-stake documents, like contracts, tax filings, and compliance records.
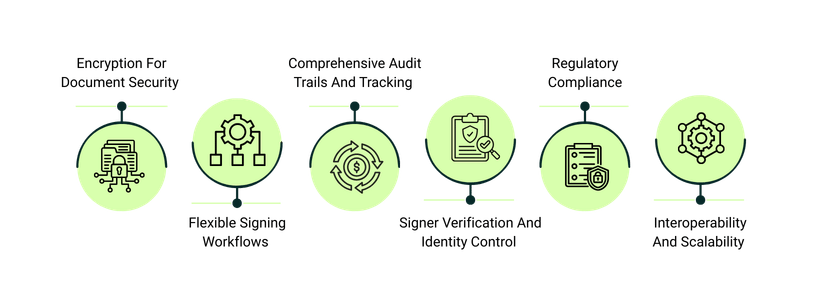
Core Functionalities Of Digital Signature
Examples Of Digital Signature Applications
An electronic signature is any digital approach that shows approval or consent on a document. In comparison to digital signatures, it does not use encryption or a certificate to verify a signer’s identity. It can be as simple as clicking the ‘I Agree’ button, entering your name, or uploading a scanned photo of your signature.
Electronic signatures are commonly used in business workflows, where quick turnaround and simplicity are more important than advanced verifications. These are generally used for internal approvals, HR documents, sales agreements, and client onboarding forms.
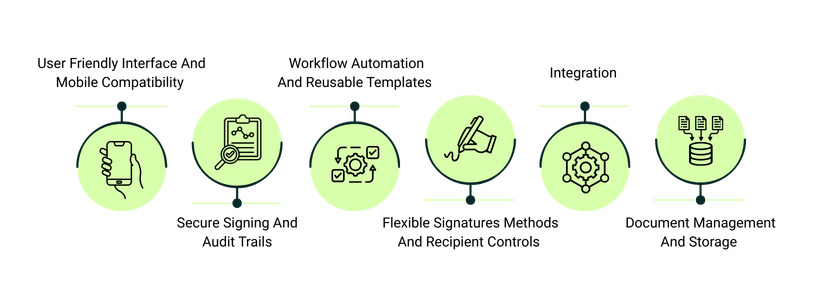
Core Functionalities Of An Electronic Signature
Example Of Electronic Signature Use Cases
When you are to decide between a digital signature and an electronic signature, you have to keep in mind what is the nature of your documents, and the security standards you need to meet, and how closely your work is related to compliance obligations. Once you realize how these two technologies differ, it will be easy to opt for the option that gives you the best value.
Choose Digital Signature When:
- You work with confidential or classified documents, like healthcare forms, tax returns, or contracts, that require proof of identity and document integrity
- Your organization requires strong legal enforceability, including tamper-proof audit trails and cryptographic verification
- You need to meet safety and legal compliance standards with every signature, such as eIDAS (electronic Identification, Authentication and Trust Services) or ESIGN
- Your documents must be trusted across jurisdictions and require regulatory investigation
Choose Electronic Signature When:
- You prioritize quick approvals for low-risk documents, like internal HR forms, vendor agreements, and client onboarding
- The required features include ease of use, minimal technical setup, and cloud-based accessibility
- Your workflows demand efficiency and convenience, with no need for advanced cryptographic verification
- You manage documents where proof of intent is sufficient, and advanced compliance or audit requirements are not required
The choice for you to go after a digital signature or an electronic signature is a pretty straight forward one. It is basically based on the type of documents you handle, and the level of legal security you need. Digital signatures bring more value to high-risk or regulated documents that need identity verification and document integrity.
Electronic signatures are more suitable for routine approvals, internal operations, and agreements where convenience and speed are the top priorities. You have to match your preference with your security requirements and compliance obligations to help you make the signing processes smooth and legally binding.