Kanban is a visual signaling system that helps manage workflow, especially in environments where production is triggered by demand rather than by a predetermined schedule. This approach is highly essential when using kanban in manufacturing, as it helps reduce waste and enhance efficiency, aligning with the principles of lean manufacturing.
However, utilizing Kanban properly requires a bit of foresight and lessons in practicality. Thus, in this article, we’re going to cover how to use it properly used and implement it within manufacturing industries.
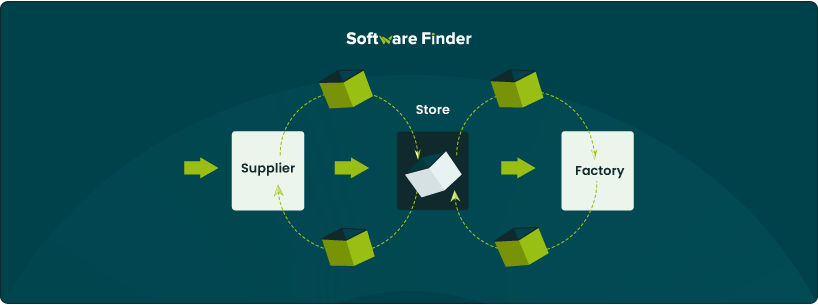
Lean manufacturing aims to maximize output by minimizing waste. As part of this approach, the Kanban framework plays a crucial role in managing workflow. Kanban is designed to create a smooth flow of materials that are just enough to complete each task. This helps maintain productivity while minimizing excess inventory and reducing delays.
Kanban cards track the progress of a specific item. When an item is moved to the next stage of production, the Kanban card is also moved with it. Thus, both keep moving across the production line until they are finished.
Once an item has passed a certain phase of production, a new order for replenishment of the same item is placed. New materials are then delivered to produce a new item, and the process of moving that item along the stages of production begins again. This ‘pull’ system, as opposed to a ‘push’ system, allows companies to control their inventory and produce required products based on demand.
Additionally, Kanban also focuses on kaizen—a mindset that champions continuous improvement. In the context of lean manufacturing, this involves making constant small incremental changes to the workflow until optimal production capacity has been achieved.
 Let’s look at some Kanban board examples in a typical manufacturing process to better understand how Kanban is used in this industry.
Let’s look at some Kanban board examples in a typical manufacturing process to better understand how Kanban is used in this industry.
The Kanban board above is split into four columns that denote various stages of production. Each column holds tasks that are all within that production stage. However, once a task is finished with its requirement, it moves from one column to the next. Once it reaches the last column and finishes its requirement, the task is taken off the board.
This type of visual representation allows managers to have a bird’s eye view of the entire process, allowing them to monitor and track progress. They can also determine which tasks need to be completed urgently, making it easy to take the necessary decisions accordingly.
Since Kanban espouses many principles from lean manufacturing, it’s a natural tool that can help any company establish lean manufacturing practices. However, its usefulness can be hampered by other external factors such as demand fluctuations and company culture. Additionally, implementing Kanban can be challenging due to its inherent complexity, particularly for companies using it for the first time.
Therefore, managers must consider everything before trying to implement Kanban boards in their workflows. They can also consider various solutions to mitigate these challenges such as providing training for Kanban systems and various other standardized practices.
